Microsoft Windows Server 2016 has been a popular choice for businesses for years, providing a stable and secure environment for servers and applications. However, all good things must come to an end, and so does the support for this version of Windows Server. If you’re still using Windows Server 2016 in your organization, it’s crucial to understand the Windows Server 2016 End of Life (EOL) process and what you need to do to protect your systems and ensure smooth operations.
In this article, we will break down everything you need to know about Windows Server 2016’s EOL and provide tips on how to make the transition to newer versions.
- Upgrade to Windows Server 2025 to stay current with the latest features.
Table of Contents
What Does Windows Server 2016 End of Life Mean?
When Microsoft announces the end of life for any software, including Windows Server 2016, it means that the company will stop providing support for the product. This includes security updates, bug fixes, and technical support. Once the support ends, the software becomes more vulnerable to security threats, as no more patches will be released.
For Windows Server 2016, the end of mainstream support occurred in January 2022, and extended support will end in January 2027. After this date, your systems will no longer receive critical updates, leaving them exposed to potential risks.
The end of life for Windows Server 2016 is a significant event for businesses using this version of the software. Here’s why:
- Security Risks: Without regular updates, your system becomes a target for cyberattacks. Security vulnerabilities that are discovered after the EOL date won’t be patched.
- Compliance Issues: Many industries have strict regulatory requirements, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Using unsupported software could lead to compliance violations and penalties.
- Operational Disruptions: Running outdated software may cause compatibility issues with new hardware, software, or cloud services. It can also make it harder to troubleshoot problems as Microsoft will no longer offer support.
- Missed Features and Improvements: Newer versions of Windows Server come with advanced features, better performance, and greater security. Not upgrading means missing out on these benefits.
Explore Windows Server 2019′s end of life and upgrade paths
What Happens After Windows Server 2016 Reaches End of Life?
Once Windows Server 2016 reaches the end of its extended support in 2027, users can expect the following:
- No More Security Updates: Your server will no longer receive patches to fix security flaws.
- No More Technical Support: Microsoft will no longer assist you with troubleshooting or resolving issues with the software.
- Limited Compatibility: Many new software tools and applications may no longer work with Windows Server 2016.
Options for Businesses After Windows Server 2016 End of Life
As a business, there are a few different paths you can take to ensure your IT environment remains secure and efficient after the EOL date:
1. Upgrade to a Newer Version of Windows Server
The most straightforward option is to upgrade to a newer version of Windows Server. Some of the most popular choices include:
- Windows Server 2019: This version offers improved security features, better performance, and updated functionalities.
- Windows Server 2022: The latest release with enhanced security, hybrid cloud capabilities, and better container support.
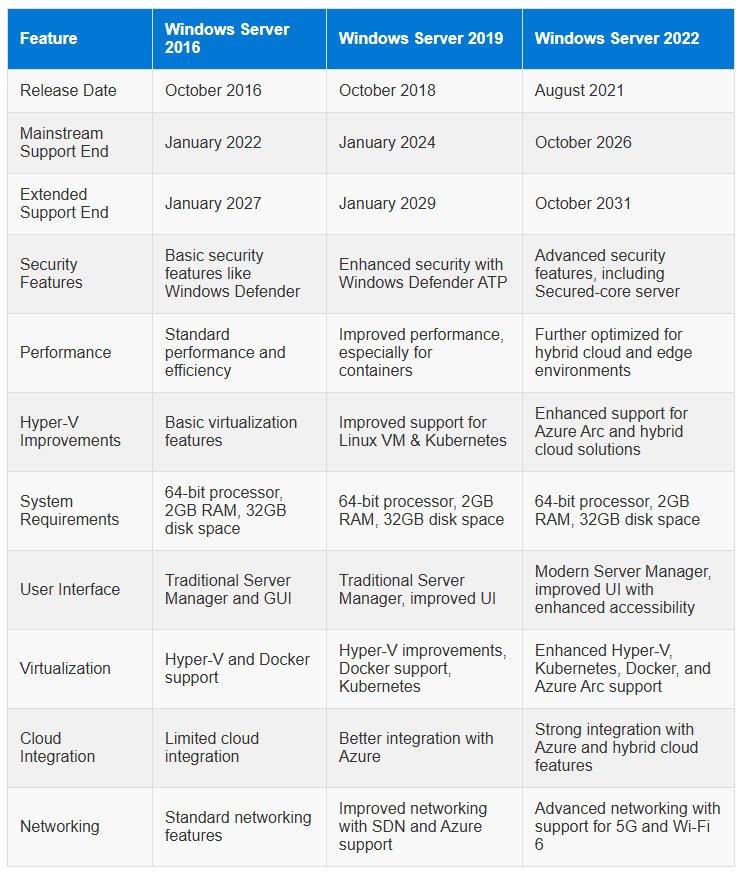
Upgrading to one of these versions ensures that you continue to receive regular updates and support.
2. Consider Cloud Solutions
Another option is to move your operations to the cloud. Platforms like Microsoft Azure allow businesses to migrate their services without the need for on-premises servers. This option reduces the burden of managing physical servers and provides better scalability and flexibility.
3. Stay on Windows Server 2016 (Not Recommended)
If upgrading isn’t feasible immediately, you could choose to stay on Windows Server 2016 even after support ends. However, this is not recommended due to the risks mentioned earlier, such as security vulnerabilities and compliance violations.
How to Upgrade from Windows Server 2016
If you’ve decided to upgrade, here are the steps to follow:
Step 1: Assess Your Current System
- Evaluate Hardware: Ensure that your current hardware can support a newer version of Windows Server.
- Check Software Compatibility: Review the software and applications running on your server to ensure they are compatible with the new version.
Step 2: Backup Your Data
Before performing any upgrade, make sure to backup all critical data to prevent loss in case of errors during the process.
Step 3: Install the New Version
You can perform an in-place upgrade or a clean installation, depending on your preference and system requirements. An in-place upgrade will preserve your settings, while a clean installation will give you a fresh start.
Step 4: Verify Post-Upgrade
After the upgrade, verify that everything works correctly, and all applications are running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens if I continue using Windows Server 2016 after the end of life?
Continuing to use Windows Server 2016 after the end of life means your system will be exposed to security risks as there will be no more updates. You may also face compatibility and compliance issues.
How can I upgrade from Windows Server 2016?
You can upgrade to a newer version of Windows Server, such as Windows Server 2019 or Windows Server 2022, or consider moving to a cloud-based solution like Microsoft Azure. Always ensure that your hardware and software are compatible before upgrading.
Is it safe to stay on Windows Server 2016 after the end of life?
It is not recommended to stay on Windows Server 2016 after the end of life, as it will no longer receive security patches or technical support. This increases the risk of cyberattacks and system failures.
Can I still get support for Windows Server 2016 after the end of life?
After the end of life, Microsoft will no longer offer free support for Windows Server 2016. However, you may be able to purchase Extended Security Updates (ESU) from Microsoft for a limited time, but this is an expensive and temporary solution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Windows Server 2016 end of life is something that every organization using this version should take seriously. It’s important to understand the risks associated with continuing to use unsupported software and plan accordingly. Upgrading to a newer version of Windows Server or migrating to the cloud are the best options to ensure that your business remains secure and compliant.