Table of Contents
In today’s digital age, managing your company’s network and users is crucial. One of the most common solutions used for this task is Active Directory (AD). It’s a directory service that helps manage users, computers, and other resources within an organization’s IT infrastructure.
In this article, we’ll compare two primary methods of implementing Active Directory—On-premise Active Directory and Cloud-based Active Directory (Azure AD). Understanding the differences can help you decide which solution best fits your organization’s needs.
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD) is a technology from Microsoft that stores and organizes information about resources in a network. It helps to manage users, groups, permissions, and devices, allowing IT administrators to control access to resources and services in the organization.
There are two types of AD: on-premise and cloud-based. Let’s dive into the details to understand which option might be better for your business.
- Find the main differences between SQL Server editions
On-Premise Active Directory
On-premise Active Directory refers to the traditional AD setup, where all servers and infrastructure are physically located within your organization. You own, maintain, and control the servers, making it ideal for businesses that prefer to keep their infrastructure within their premises.
Benefits of On-Premise Active Directory
- Full Control: You have complete control over the environment and security settings.
- Customization: You can tailor the infrastructure to meet your specific business needs.
- Offline Accessibility: Works without an internet connection, ideal for businesses with poor or no internet access.
- Security: Your IT team directly handles the security of the infrastructure.
Drawbacks of On-Premise Active Directory
- High Maintenance: You must manage hardware, updates, and security patches.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling up requires more physical hardware, which can be expensive.
- Costs: The initial setup and maintenance costs can be high.
Cloud-Based Active Directory (Azure AD)
On the other hand, Cloud-based Active Directory (Azure AD) is a cloud solution provided by Microsoft through its Azure platform. Unlike on-premise AD, Azure AD does not require any physical hardware. It’s hosted in the cloud, and users can access their resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
Benefits of Cloud-Based Active Directory
- Lower Costs: No need to invest in physical hardware or infrastructure.
- Scalability: You can easily scale the system up or down based on your needs.
- Remote Access: Users can access resources from anywhere, which is perfect for remote work.
- Automatic Updates: Microsoft manages updates, security patches, and maintenance, reducing the IT burden.
- Integration with Office 365: Azure AD works seamlessly with Microsoft Office 365 and other cloud services.
Drawbacks of Cloud-Based Active Directory
- Dependence on Internet Connection: Requires a reliable internet connection to function.
- Less Control: You have less direct control over the infrastructure and security settings.
- Data Privacy: Some businesses are concerned about storing sensitive data off-site in the cloud.
On-Premise Active Directory vs. Cloud-Based Active Directory: Key Differences
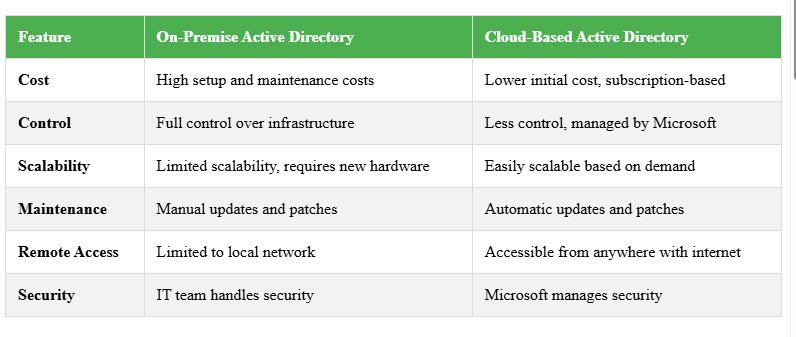
Why Choose One Over the Other?
Understand which Windows Server edition fits your Active Directory needs.
When to Choose On-Premise Active Directory
- Large Organizations: If your company has a large IT team and wants to maintain full control over its infrastructure, on-premise AD may be the right choice.
- Sensitive Data: If you handle sensitive data and prefer to keep it in-house, on-premise AD offers greater security and control.
- Poor Internet Connectivity: Businesses with unreliable or no internet access may prefer an on-premise solution.
When to Choose Cloud-Based Active Directory (Azure AD)
- Small to Medium Businesses: Azure AD is ideal for businesses with limited IT resources. It is cost-effective and easy to manage.
- Remote Work: If your employees work from different locations, cloud-based AD offers the flexibility and remote access you need.
- Scalability Needs: For growing businesses, Azure AD’s scalability allows you to adjust the service as per your needs without investing in more hardware.
Hybrid Approach: Combining On-Premise and Cloud-Based Active Directory
For many organizations, a hybrid model may be the best solution. This involves integrating both on-premise and cloud-based AD to meet the specific needs of the business. The hybrid model allows you to maintain critical workloads on-premise while taking advantage of the cloud’s flexibility and cost-effectiveness for less sensitive applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between Active Directory and Azure Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD) is the on-premise solution, while Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is the cloud version of AD. Azure AD allows you to access resources online, whereas AD is typically used for managing resources within an organization’s local network.
Can I use both On-premise AD and Azure AD together?
Yes, you can use both through a hybrid setup. This allows businesses to manage their existing on-premise resources while also leveraging the flexibility of Azure AD for cloud services.
Which option is more secure: On-Premise AD or Azure AD?
Both solutions have strong security measures in place. On-premise AD allows your IT team to manage security directly, while Azure AD benefits from Microsoft’s extensive security infrastructure and automatic updates.
How do I migrate from On-Premise AD to Azure AD?
Migrating from on-premise AD to Azure AD typically involves synchronizing your on-premise directory with Azure AD using tools like Azure AD Connect. This process allows you to keep your existing on-premise resources while transitioning to the cloud.
Conclusion
Choosing between on-premise Active Directory and cloud-based Active Directory (Azure AD) depends on your organization’s size, budget, and needs. While on-premise AD provides full control and security, Azure AD offers flexibility, lower costs, and easier scalability. Many businesses opt for a hybrid solution, combining the best of both worlds.
By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of both options, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your organization’s IT strategy.